The Motives for European Imperialism

Many countries in history expanded and developed massive empires through a policy of imperialism. Imperialism occurs when a stronger nation takes over or dominates a weaker nation or region. Larger, more powerful nations used political, economic, or military force to do this.
The period between the 18th and 20th centuries in European history is known as the Age of Imperialism.
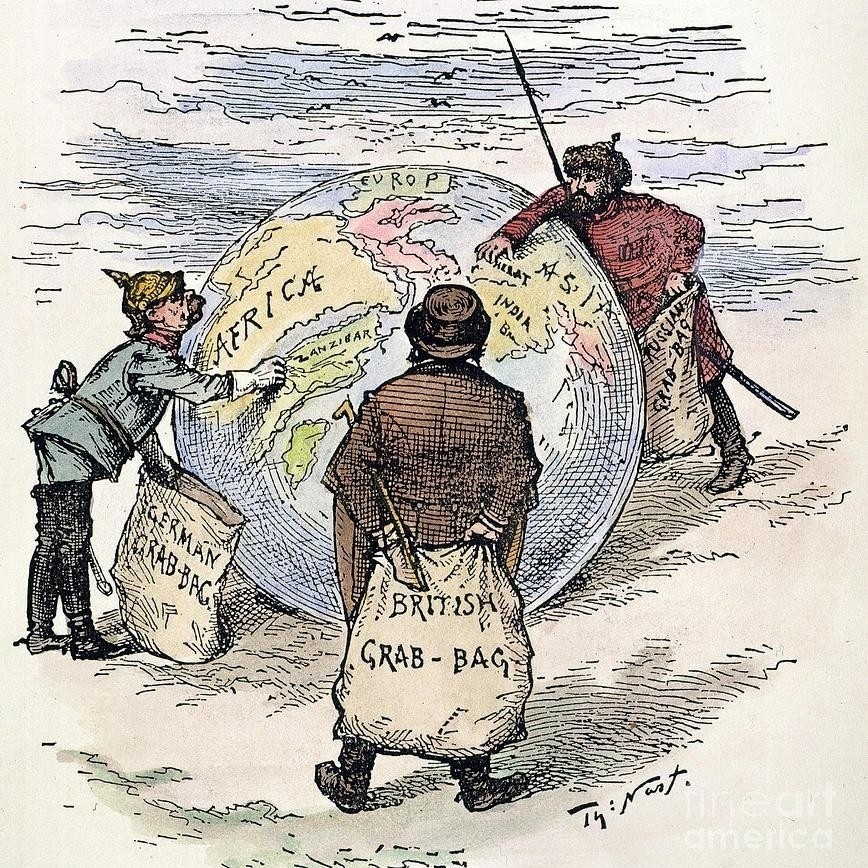
The most active European countries in terms of imperialism were Britain, France, and Germany.
In the late 1800’s, economic, political, and religious motives prompted these nations to expand their influence over other regions, each with a goal to increase their power across the globe.
The Industrial Revolution of the 1800’s created a need for natural resources to fuel newly invented machinery and transportation. Resources like coal, iron, and rubber were in high demand. Some nations did not have enough raw materials to support their industrialization and looked to other lands to find them.
Expanding outside of its borders also allowed a country to enter foreign markets for the purpose of selling industrial goods. Traditional industries became displaced as manufacturing and markets moved to foreign countries. One such company, the British East India Company, became highly profitable by obtaining natural resources in India and selling goods in markets throughout the world.
Imperialism was also influenced by nationalism, a sense of pride in one’s country. People were proud of their growing countries and their accomplishments. A famous saying from that time was, “the sun never sets on the British Empire”, meaning that the British empire was so vast that there was always a territory that had sun shining on it. This created a sense of competition among European countries to show off their power and prestige around the world. This competition ignited already heated tensions between European countries and conflicts began to spread.
Imperialism is not only political and economic, but also cultural. When European powers took over foreign lands, they felt superior to the natives. They looked down on indigenous civilizations and felt that they needed to bring western culture and “civilize” and educate the “savage” population. This was often called the “White Man’s Burden”.
Religion was an important part of imperialism as well. Christian missionaries looked to convert native people to Christianity and also called for an end to slave trade in hopes Africa so it could become part of western civilization.
Of course, this imperialism had a devastating impact on millions of people across the globe. Innocent people across Asia and Africa in particular endured untold suffering at the hands of invading European powers. They often fought back as you will see in the coming sections.